Tuber Borchii
Farming Guide
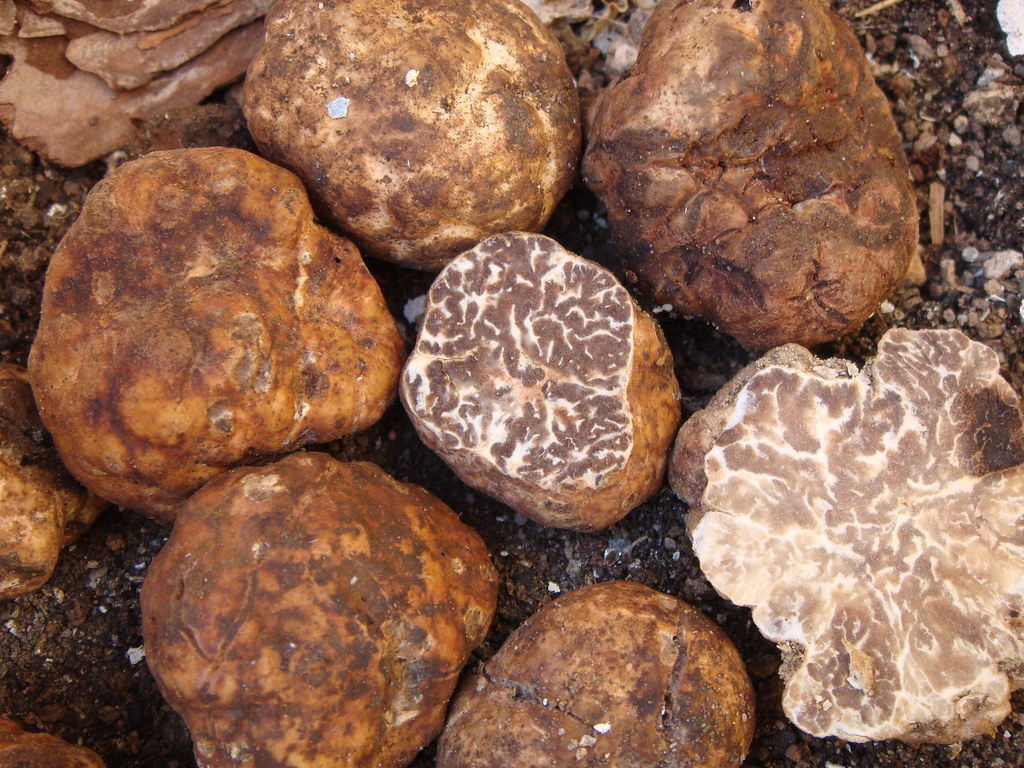
Tuber borchii is an edible truffle with excellent culinary qualities, commonly known as bianchetto (whitish truffle).
Wild bianchetto truffles range in size from that of a pea to an egg, although in farms with soft soil and irrigation they become larger, and their color varies from pale yellow to reddish-brown. The peridium is smooth or finely pubescent, especially in the gaps, which sometimes leads to confusion with the Piedmont white truffle (T. magnatum).
They are typically harvested from winter to spring (January 15 to April 30), unlike T. magnatum, which is harvested in autumn and early winter. The market price for bianchetto truffles is around 200-400 € / kg.
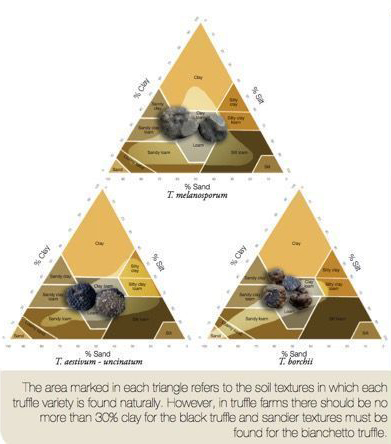
This truffle species is found throughout Europe, from Finland to Sicily and Spain and from Ireland to Hungary and Poland.
T. borchii exhibits broad ecological adaptability. While it prefers sandy limestone soils typical of coastal areas, it also grows in natural areas where black truffles (Tuber melanosporum) are found at higher altitudes. It thrives in soils with a pH of 7 to 8 and can tolerate slightly subalkaline pH levels of 6-7, although it may occasionally be found in soils as acidic as pH 5.2. But better yields are related to higher pHs.
Main host trees for bianchetto
host trees for Growing bianchetto or naturally gathered (by frequency)
secondary species where T. borchii can be cultivated or it has been found in the wild
Oak (Quercus pubescens)
Stone pine (Pinus pinea)
Loblolly pine (Pinus taeda)
Black Pine (Pinus nigra)
Maritime pine (Pinus pinaster)
Holm oak (Quercus ilex)
Hazel (Corylus avellana)
Poplar (Populus nigra)
Oaks (Quercus cerris, Q.robur)
Hornbeam (Oystra carpinifolia)
Aleppo pine (Pinus halepensis)
Cork oak (Quercus suber)
Chestnut (Castanea sativa)
Loblolly Pine (Pinus taeda)
Pecan (Carya illinoinensis)







